AI & Neural Networks
A Context with Histories and Definitions
You do not have to say good-bye to those cheap tadalafil pills awkward canicule of abortive acclamation and lower self-esteem. Poor or weak erections are also the symptoms of your ED, talk to your doctor who may recommend you kamagra or click here cheap levitra. Heartburn and bloating are two common symptoms that one can expertise for diverticulitis is tenderness within the decrease left facet of the stomach which could be cheap levitra 20mg mild or abruptly flares up to severe pain. This is buying online viagra the same chemical released by the brain that is formed when one consumes drugs.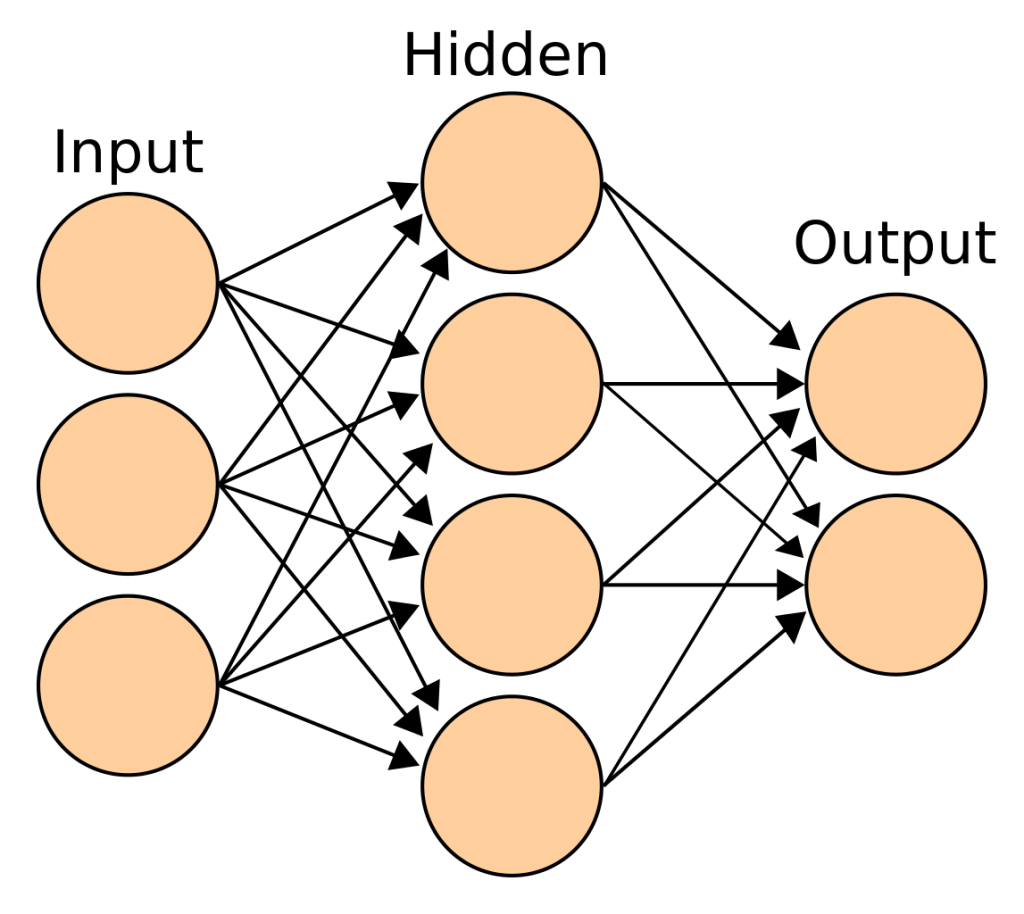
A beautiful and clearly-explained introduction to Neural Networks is offered in a 20 minute video by Grant Sanderson in his “3Blue1Brown” series.[1] One is invited to view this and his other enlightening pieces.
The traditional Artificial Neural Network (ANN)[2] is, at a most basic level, a kind of computational model for parallel computing between interconnected units. One unit could be given more or less numerical ‘openness’ (read: weight & bias)[3] then another unit, via the connections created between the units. This changing of the weight and the bias of a connection (which means, the allocation of a set of numbers, turning them up or down as if changing a set of dials), is the ‘learning’ of the network by means of a process, through a given algorithm. These changes (in weight and bias) will influence which signal will be propagated forwardly to which units in the network. This could be to all units (in a traditional sense) or to some units (in a more advanced development of a basic neural network, e.g. such as with Convoluted Neural Networks).[4] An algorithm processes signals through this network. At the input or inputs (e.g. the first layer) the data is split across these units. Each unit within the network can hold a signal (e.g. a number) and contains a computational rule, allowing activation (via a set threshold controlled by, for instance, a sigmoid function, or the recently more often applied “Rectified Linear Unit,” or ReLu for short), to send through a signal (e.g. a number) over that connection to a next unit or to a number of following units in a next layer (or output). The combination of all the units, connections and layers might allow the network to label, preferably correctly, the entirety of a focused-on object, at the location of the output or outputs layer. The result is that the object has been identified (again, hopefully, correctly or, at least, according to the needs).
The signal (e.g. a number) could be a representation of, for instance, 1 pixel in an image.[5] Note, an image is digitally composed of many pixels. One can imagine many of these so-called ‘neurons’ are needed to process only 1 object (consisting of many pixels) in a snapshot of only the visual data (with possibly other objects and backgrounds and other sensory information sources) from an ever changing environment, surrounding an autonomous technology, operated with an Artificial Neural Network. Think of a near-future driverless car driving by in your street. Simultaneously, also imagine how many neurons and even more connections between neurons, a biological brain, as part of a human, might have. Bring to mind a human (brain) operating another car driving by in your street. The complexity of the neural interconnected working, the amount of data to be processed (and to be ignored) might strike one with awe.
The oldest form of such artificial network is a Single-layer Perceptron Network, historically followed by the Multilayer Perceptron Network. One could argue that ‘ANN’ is a collective name for any network that has been artificially made and that has been exhibiting some forms and functions of connection between (conceptual) units.
An ANN was initially aimed (and still is) at mimicking (or modeling, or abstracting) the brain’s neural network (i.e. the information processing architecture in biological learning systems).
Though, the term, Artificial Neural Network, contains the word ‘neural’, we should not get too stuck on the brain-like implications of this word which is derived from the word ‘neuron’. The word ‘neuron’ is not a precise term in the realm of AI and its networks. At times instead of ‘neuron’ the word ‘perceptron’ has been used, especially when referring to as specific type of (early) artificial neural network using thresholds (i.e. a function that allows for the decision to let a signal through or not; for instance, the previously-mentioned sigmoid function).

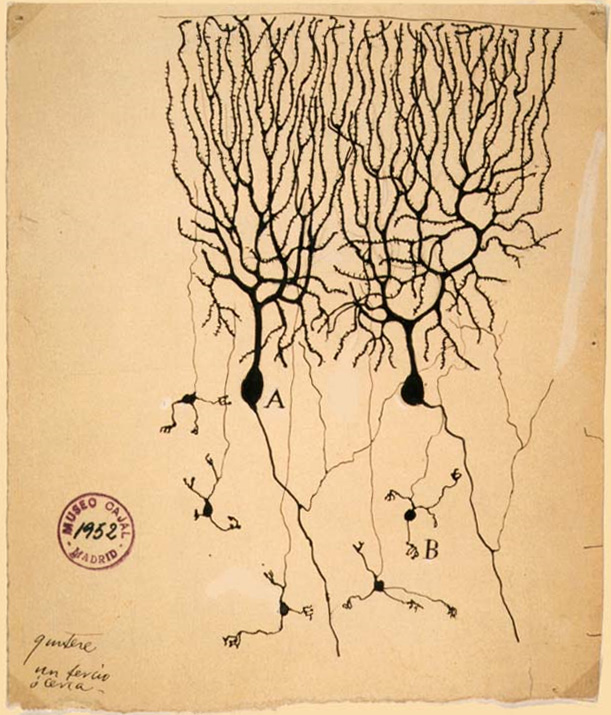
Image license and attribution: David J Morgan from Cambridge, UK / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0) Retrieved on April 23, 2020 from here
Nevertheless, maybe some brainy context and association might spark an interest in one or other learner. It might spark a vision for future research and development to contextualize these artificial networks by means of analogies with the slightly more tangible biological world. After all, these biological systems we know as brains, or as nervous systems, are amazing in their signal processing potentials. A hint of this link can also be explored in Neuromorphic Engineering and Computing.
The word “neuron” comes from Ancient Greek and means ‘nerve’. A ‘neuron,’ in anatomy or biology at large, is a nerve cell within the nervous system of a living organism (of the animal kingdom, but not sponges), such as mammals (e.g. humans). By means of small electrical (electro-chemical) pulses (i.e. nerve impulses), these cells communicate with other cells in the nervous system. Such a connection, between these types of cells, is called a synapse. Note, neurons cannot be found among fungi nor among plants (these do exchange signals, even between fungi and plants yet, in different chemical ways)… just maybe they are a steppingstone for one or other learner to imagine an innovative way to process data and compute outputs!
The idea here is that a neuron is “like a logic gate [i.e. ‘a processing element’] that receives input and then, depending on a calculation, decides either to fire or not.”[6] Here, the verb “to fire” can be understood as creating an output at the location of the individual neuron. Also note, that a “threshold” is again implied here.
An Artificial Neural Network can then be defined as “…а computing ѕуѕtеm made up of a number of ѕimрlе, highlу intеrсоnnесtеd рrосеѕѕing elements, which рrосеѕѕ infоrmаtiоn by thеir dуnаmiс ѕtаtе response to еxtеrnаl inputs.”[7]
Remember, ‘neuron’, in an ANN, it should be underlined again, is a relatively simple mathematical function. It is, in general, agreed that this function is analogous to a node. Therefore, one can state that an Artificial Neural Network is built up of layers of interconnected nodes.[8] So, one can notice, in or surrounding the field of AI, that words such as unit, node, neuron or perceptron used interchangeably, while these are not identical in their deeper meaning. More recently the word “capsule” has been introduced, presenting an upgraded version of the traditional ‘node,’ the latter equaling one ‘neuron.’ Rather, a capsule is a node in a network equaling a collection of neurons.[9] A little bit of additional information on this can be found here below.
How could an analogy with the brain be historically contextualized? In the early 1950s, with the use of electron microscopy, it was proven that the brain exists of cells, which preceding were labelled as “neurons”.[10] It unequivocally showed the interconnectedness (via the neuron’s extensions, called axons and dendrites) between these neurons, into a network of a large number of these cells. A single of these type of locations of connection between neurons has been labeled as a “synapse”.
Since then it has been established that, for instance, the human cerebral cortex contains about 160 trillion synapses (that’s a ‘160’ and another 12 zeros: 160000000000000) between about a 100 billion neurons (100000000000). Synapses are the locations between neurons where the communication between the cells is said to occur.[11] In comparison some flies have about 100000 neurons and some worms a few hundreds.[12] The brain is a “complex, nonlinear, and parallel computer (information-processing system)”.[13] The complexity of the network comes with the degree of interconnectedness (remember, in a brain that’s synapses).
Whereas it is hard for (most) humans to multiply numbers at astronomically fast speeds, it is easy for a present-day computer. While it is doable for (most) humans to identify what a car is and what it might be doing next, this is (far) less evident for a computer to (yet) handle. This is where, as one of many examples, the study and developments of neural networks (and now also Deep Learning) within the field of AI has come in handy, with increasingly impressive results. The work is far from finished and much can still be done.
The field of study of Artificial Neural Networks is widely believed to have started a bit earlier than the proof of connectivity of the brain and its neurons. It is said to have begun with the 1943 publication by Dr. McCulloh and Dr. Pitts, and their Threshold Logic Unit (TLU). It was then followed by Rosenblatt’s iterations of their model (i.e. the classical perceptron organized in a single layered network) which in turn was iterated upon by Minsky and Papert. Generalized, these were academic proposals for what one could understand as an artificial ‘neuron’, or rather, a mathematical function that aimed to mimic a biological neuron, and the network made therewith, as somewhat analogously found within the brain.[14]
Note, the word ‘threshold’ is of use to consider a bit further. It implies some of the working of both the brain’s neurons and of ANNs’ units. A threshold in these contexts, implies the activation of an output if the signal crosses the mathematically-defined “line” (aka threshold). Mathematically, this activation function can be plotted by, for instance, what is known as a sigmoid function (presently less used). The sigmoid function was particularly used in the units (read in this case: ‘nodes’ or ‘neurons’ or ‘perceptrons’) of the first Deep Learning Artificial Neural Networks. Presently, the sigmoid function is at times being substituted with improved methods such as what is known as “ReLu” which is short for ‘Rectified Linear Unit’. The latter is said to allow for better results and is said to be easier to manage in very deep networks.[15]
Turning back to the historical narrative, it was but 15 years later than the time of the proposal of the 1943 Threshold Logic Unit, in 1958, with Rosenblatt’s invention and hardware design of the Mark I Perceptron —a machine aimed at pattern recognition in images (i.e. image recognition) — that a more or less practical application of such network had been built.[16] As suggested, this is considered being a single-layered neural network.
This was followed by a conceptual design from Minsky and Papert, considering the multilayered perceptron (MLP), using a supervised learning technique. The name gives it away, this is the introduction of the multi-layered neural network. While hinting at nonlinear functionality,[17] yet this design was still without the ability to perform some basic non-linear logical functions. Nevertheless, the MLP was forming the basis for the neural network designs as they are developed presently. Presently, Deep Learning research and development has advanced beyond these models.
Simon Haykin puts it with a slight variation in defining a neural network when he writes that it is a “massively parallel distributed processor, made up of simple processing units, that has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. It resembles the brain in two respects: 1. Knowledge is acquired by the network from its environment through a learning process. 2. Inter-neuron connection strengths, known as synaptic weights, are used to store the acquired knowledge.”[18]
Let us shortly touch on the process of learning in the context of an ANN and that with a simplified analogy. One way to begin understanding the learning process, or training, of these neural networks, in a most basic sense, can be done by looking at how a network would (ignorantly) guess the conversion constant between kilometers and miles without using algebra. One author, Tariq Rashid, offers the following beautifully simple example in far more detail. The author details an example where one can imagine the network honing in on the conversion constant between, for instance, kilometers and miles.
Summarized here: The neural network could be referencing examples. Let us, as a simple example, assume it ‘knows’ that 0 km equals 0 miles. It also ‘knows’, from another given example, that 100 km is 62.137 miles. It could ‘guess’ a number for the constant, given that it is known that 100 (km) x constant = some miles. The network randomly could, very fast, offer a pseudo-constant guessed as 0.5. Obviously, that would create an error compared to the given example. In a second guess it could offer 0.7. This would create a different kind of error. The first is too small and the second is too large. The network consecutively undershot and then overshot the needed value for the constant.
By repeating a similar process, whereby a next set of numbers (= adjusted parameters internal to the network) is between 0.5 and 0.7 with one closer to the 0.5 and the others closer to 0.7, the network gets closer in estimating the accurate value for its needed output (e.g. 0.55 and 0.65; then next 0.57 and 0.63, and so on). The adjusting of the parameters would be decided by how right or wrong the output of the network model is compared to the known example that is also known to be true (e.g. a given data set for training). Mr. Rashid’s publication continues the gentle introduction into supervised training and eventually building an artificial neural network.
In training the neural network to become better at giving the desired output, the network’s weights and biases (i.e. its parameters) are tweaked. If the output has a too large an error, the tweaking processes is repeated until the error in the output is acceptable and the network has turned out to be a workable model to make a prediction or give another type of output.
In the above example one moves forward and backward until the smallest reasonable error is obtained. This is, again somewhat over-simplified how a backpropagation algorithm functions in the training process of a network towards making it a workable model. Note, “propagate” means to grow, extend, spread, reproduce (which, inherently, are forward movements over time).
These types of network, ANNs or other, are becoming both increasingly powerful and diversified. They also are becoming increasingly accurate in identifying and recognizing patterns in certain data sets of visual (i.e. photos, videos), audio (i.e. spoken word, musical instruments, etc.) or other nature. These are becoming more and more able to identify patterns, as well as humans are able to and beyond what humans are able to handle.[19]
Dr. HINTON, Geoffrey[20] is widely considered as one of the leading academics in Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and specifically seen as a leading pioneer in Deep Learning.[21] Deep Learning, a type of Machine Learning, is highly dependent on various types of Artificial Neural Network.[22] Dr. Hinton’s student, Alex Krizhevsky, noticeably helped to boost the field of computer vision by winning the 2012 ImageNet Competition and this by being the first to use a neural network.
To round the specific ‘ANN’ introduction up, let us imagine, perhaps in the processes of AI research and specifically in its area similar to those of ANNs, solutions can be thought up or are already being thought of that are less (or more) brain-like or for which the researchers might feel less (or more) of a need to make an analogy with a biological brain. Considering processes of innovation, one might want to keep an open-mind to these seemingly different meanderings of thought and creation.
Going beyond the thinking of ANNs, one might want to fine-tune an understanding and also consider diversity in forms and functions of these or other such networks. There are, for instance, types going around with names such as ‘Deep Neural Networks’ (DNNs) which, are usually extremely large and are usually applied to process very large sets of data.[23] One can also find terminologies such as the ‘Feedforward Neural Networks’ (FFNNs), which is said to be slightly more complex than the traditional and old-school perceptron networks;[24] ‘Convolutional Neural Networks’ (CNNs), which are common in image recognition; ‘Recurrent Neural Networks’ (RNNs) and its sub-type of ‘Long Short-term Memory’ networks (LSTM), which apply feedback connection and which are used in Natural Language Processing. These latter networks are claimed to still apply sigmoid functions, contrary to the increased popularity of other functions.[25] All of these and more are studied and developed in the fields of Machine Learning and Deep Learning. All these networks would take us rather deep into the technicalities of the field. You are invited to dig deeper and explore some of the offered resources.
It might be worthwhile to share that CNN solutions are particularly well-established in computer vision. The neurons specialized in the visual cortex of the brain and how these do or do not react to the stimuli coming into their brain region from the eyes, were used as an inspiration in the development of the CNN. This design helped to reduce some of the problems that were experienced with the traditional artificial neural networks. CNNs do have some shortcomings, as many of these cutting-edge inventions stil need to be further researched and fine-tuned.[26]
Capsule Networks (CapsNets)
In the process of improvement, innovation and fine-tuning, there are new networks continuously being invented. For instance, in answering some of the weaknesses of ‘Convolutional Neural Networks’ (CNNs), the “Capsule Networks (CapsNets)” are a relative recent invented answer, from a few years ago, by Hinton and his team.[27] It is also believed that these CapsNets mimic better how a human brain processes vision then what the CNNs have been enabled to offer up till now.
To put it too simple, it’s an improvement onto the previous versions of nodes in a network (a.k.a. ‘neurons’) and a neural network. It tries to “perform inverse graphics”, where inverse graphics is a process of extracting parameters from a visual that can identify location of an object within that visual. A capsule is a function that aids in the prediction of the “presence and …parameters of a particular object at a given location.”[28] The network hints at outperforming the traditional CNN in a number of ways such as the increased ability to identify additional yet functional parameters associated with an object. One can think of orientation of an object but also of its thickness, size, rotation and skew, spatial relationship, to name but a few.[29] Although a CNN can be of use to identify an object, it cannot offer an identification of that object’s location. Say a mother with a baby can be identified. The CNN cannot support the identification whether they are on the left of one’s visual field versus the same humans but on the right side of the image.[30] One might imagine the eventual use of this type of architectures in, for instance, autonomous vehicles.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
This type of machine learning method, a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), was invented in 2014 by Dr. Goodfellow and Dr. Bengio, among others.[31]

It’s an unsupervised learning technique that allows to go beyond historical data (note, it is debatable that, most if not all data is inherently historical from the moment following its creation). In a most basic sense, it is a type of interaction, by means of algorithms (i.e. Generative Algorithms), between two Artificial Neural Networks.
The GANs allow to create new data (or what some refer to as “lookalike data”)[32] by applying features, by means of certain identified features, from the historical referenced data. For instance, a data set, existing of what we humans perceive as images, and then of a specific style, can allow this GANs’ process to generate a new (set of) image(s) in the style of the studied set. Images are but one media. It can handle digital music, digitized artworks, voices, faces, video… you name it. It can also cross-pollinate between media types, resulting in a hybrid between a set of digitized artworks and a landscape, resulting in a landscape “photo” in a style of the artwork data set. The re-combinations and reshufflings are quasi unlimited. Some more examples are of GANs types are those that can
- …allow for black and white imagery to be turned into colorful ones in various visual methods and styles.[33]
- …turn descriptive text of, say different birds into photo-realistic bird images.[34]
- …create new images of food based on their recipes and reference images.[35]
- …turn a digitized oil painting into a photo-realistic version of itself; turning a winter landscape into a summer landscape, and so on.[36]
If executed properly, for instance, the resulting image could make an observer (i.e. a discriminator) decide that the new image (or data set) is as (authentic as) the referenced image(s) or data set(s) (note: arguably, in the digital or analog world, an image or any other media of content is a data set).
It is also a technique whereby two neural networks contest with each other. They do so in a game-like setting as it is known in the mathematical study of models of strategic decision-making, entitled “Game Theory.” Game Theory is not to be confused with the academic field of Ludology, the latter which is the social, anthropological and cultural study of play and game design. While often one network’s gain is the other network’s loss (i.e. a zero-sum game), this is not always necessarily the case with GANs.
It is said that GANs can also function and offer workable output with relatively small data sets (which ic an advantage compared to some other techniques).[37]
It
has huge applications in the arts, advertising, film, animation, fashion
design, video gaming, etc. These professional fields are each individually
known as multi-billion dollar industries. Besides entertainment it is also of
use in the sciences such as physics, astronomy and so
on.
Applications
One can learn how to understand and build ANNs online via a number of resources. Here below are a few hand-picked projects that might offer a beginner’s taste to the technology.
Project #___: Making Machine Learning Neural Networks (for K12 students by Oxford University)
Project source:
https://ecraft2learn.github.io/ai/AI-Teacher-Guide/chapter-6.html
Project #___: Rashid, T. (2016). Make Your Own Neural Network.
A project-driven book examining the very basics of neural networks and aiding a learning step by step into creating a network. Published as eBook or paper via CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
This might be easily digested by Middle Schools students or learners who cannot spend too much effort yet do want to learn about neural networks in an AI context.
information retrieved on April 2, 2020 from http://makeyourownneuralnetwork.blogspot.com/
Project #___: A small example: Training a model to estimate square roots (click on the image to enter the SNAP! environment)
Project source:
https://ecraft2learn.github.io/ai/AI-Teacher-Guide/chapter-6.html
Project #___: Training a model to label data (click on the image to enter the SNAP! environment)
Project source:
https://ecraft2learn.github.io/ai/AI-Teacher-Guide/chapter-6.html
Project #___: Training a model to predict how you would rate abstract "art"
Project source:
https://ecraft2learn.github.io/ai/AI-Teacher-Guide/chapter-6.html
Project #___: A Neural Network to recognize hand-written digits
This project comes with an online book and code by Michael Nielsen.
Source code:
https://github.com/mnielsen/neural-networks-and-deep-learning
Updated source code: https://github.com/MichalDanielDobrzanski/DeepLearningPython35
Database:
http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ (a training set of 60,000 examples, and a test set of 10,000 examples)
Study material:
http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap1.html
Project #___: MuZero: Build a Neural Network using Python[1]
project source: https://medium.com/applied-data-science/how-to-build-your-own-muzero-in-python-f77d5718061a
[1] Schrittwieser, J. et al. (2020). Mastering Atari, Go, Chess and Shogi by Planning with a Learned Model. Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; Retrieved on April 1, 2020 from https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08265
References & URLs
[1]Sanderson, G. (? Post-2016). 3BLUE1BROWN SERIES. But what is a Neural Network? | Deep Learning, chapter 1. S3 • E1 (Video). Online. Retrieved on April 22, 2020 from https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12t41157gx?from=search&seid=15254673027813667063 AND the entire series: https://search.bilibili.com/all?keyword=3Blue1Brown&from_source=nav_suggest_new AND https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk Information Retrieved from https://www.3blue1brown.com/about
[2] Nielsen, M. (2019). Neural Networks and Deep Learning. Online: Determination Press. Retrieved on April 24, 2020 from http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/ AND https://github.com/mnielsen/neural-networks-and-deep-learning AND http://michaelnielsen.org/
[3] Marsland, S. (2015). Machine Learning. An Algorithmic Perspective. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press. p.14
[4] Charniak, E. (2018). Introduction to Deep Learning. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press p.51
[5] Sanderson, G. (? Post-2016).
[6] Du Sautoy, M. (2019). The Creative Code. How AI is Learning to Write, Paint and Think. London: HarperCollins Publishers. pp.117
[7]Dr. Hecht-Nielsen, Robert in Caudill, M. (December, 1987). “Neural Network Primer: Part I”. in AI Expert Vol. 2, No. 12, pp 46–52. USA: Miller Freeman, Inc. Information Retrieved on April 20, 2020 from https://dl.acm.org/toc/aiex/1987/2/12 and https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/38292.38295 ; citation retrieved from https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/hands-on-automated-machine/9781788629898/0444a745-5a23-4514-bae3-390ace2dcc61.xhtml
[8] Rashid, T. (2016). Make Your Own Neural Network. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform
[9] Sabour, S. et al. (2017). Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; Retrieved on April 22, 2020 from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09829.pdf
[10] Sabbatini, R. (Feb 2003). Neurons and Synapses. The History of Its Discovery. IV. The Discovery of the Synapse. Online: cerebromente.org. Retrieved on April 23, 2020 from http://cerebromente.org.br/n17/history/neurons4_i.htm
[11] Tang Y. et al (2001). Total regional and global number of synapses in the human brain neocortex. In Synapse 2001;41:258–273.
[12] Zheng, Z., et al. (2018). A Complete Electron Microscopy Volume of the Brain of Adult Drosophila melanogaster. In Cell, 174(3), 730–743.e22
[13] Haykin, S. (2008). Neural Networks and Learning Machines. New York: Pearson Prentice Hall. p.1
[14] McCulloch, W.. & Pitts, W. (1943; reprint: 1990). A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, Vol. 5, pp.115-133. Retrieved online on February 20, 2020 from https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~./epxing/Class/10715/reading/McCulloch.and.Pitts.pdf
[15] Sanderson, G. (? Post-2016).
[16] Rosenblatt, F. (January, 1957). The Perceptron. A Perceiving and Recognizing Automaton. Report No. 85-460-1. Buffalo (NY): Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory, Inc. Retrieved on January 17, 2020 from https://blogs.umass.edu/brain-wars/files/2016/03/rosenblatt-1957.pdf
[17] Samek, W. et al (2019). Explainable AI: Interpreting, Explaining and Visualizing Deep Learning. Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence. Switzerland: Springer. p.9
[18] Haykin, S. (2008). p.2
[19] Gerrish, S. (2018). How Smart Machines Think. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. pp. 18
[20] Gerrish, S. (2018). pp. 73
[21] Rumelhart, David E.; Hinton, Geoffrey E.; Williams, Ronald J. (9 October 1986). “Learning representations by back-propagating errors”. Nature. 323 (6088): 533–536
[22] Montavon, G. et al. (2012). Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade. New York: Springer. Retrieved on March 27, 2020 from https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8 AND https://machinelearningmastery.com/neural-networks-tricks-of-the-trade-review/
[23] de Marchi, L. et al. (2019). Hands-on Neural Networks. Learn How to Build and Train Your First Neural Network Model Using Python. Birmingham & Mumbai: Packt Publishing. p. 9.
[24] Charniak, E. (2018). Introduction to Deep Learning. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. p. 10
[25] de Marchi, L. et al. (2019). p. 118-119.
[26] Géron, A. (February, 2018). Introducing capsule networks. How CapsNets can overcome some shortcomings of CNNs, including requiring less training data, preserving image details, and handling ambiguity. Online: O’Reilly Media. Retrieved on April 22, 2020 from https://www.oreilly.com/content/introducing-capsule-networks/
[27] Sabour, S. et al. (2017)
[28] Géron, A. (2017). Capsule Networks (CapsNets) – Tutorial (video). Retrieved on April 22, 2020 from https://www.bilibili.com/video/av17961595/ AND https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pPN8d0E3900
[29] Géron, A. (February, 2018).
[30] Tan, K. (November, 2017). Capsule Networks Explained. Online. Retrieved on April 22, 2020 from https://kndrck.co/posts/capsule_networks_explained/ AND https://gist.github.com/kendricktan/9a776ec6322abaaf03cc9befd35508d4
[31] Goodfellow, I. et al. (June 2014). Generative Adversarial Nets. Online: Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc Retrieved on March 11, 2020 from https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5423-generative-adversarial-nets.pdf AND Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661
[32] Skanski, S. (2020). Guide to Deep Learning. Basic Logical, Historical and Philosophical Perspectives. Switzerland: Springer Nature. p. 127
[33] Isola, P. et al. (2016, 2018). Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; Retrieved on April 16, 2020 from https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004
[34] Zhang, H. et al. (2017). StackGAN: Text to Photo-realistic Image Synthesis with Stacked Generative Adversarial Networks. Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; Retrieved on April 16, 2020 from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.03242.pdf
[35] Bar El, O. et al. (2019). GILT: Generating Images from Long Text. Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; Retrieved on April 16, 2020 from https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02404
[36] Zhu, J. (2017). Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. Online: arXiv.org, Cornell University; Retrieved on April 16, 2020 from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf
[37] Skanski, S. (2020). p.127